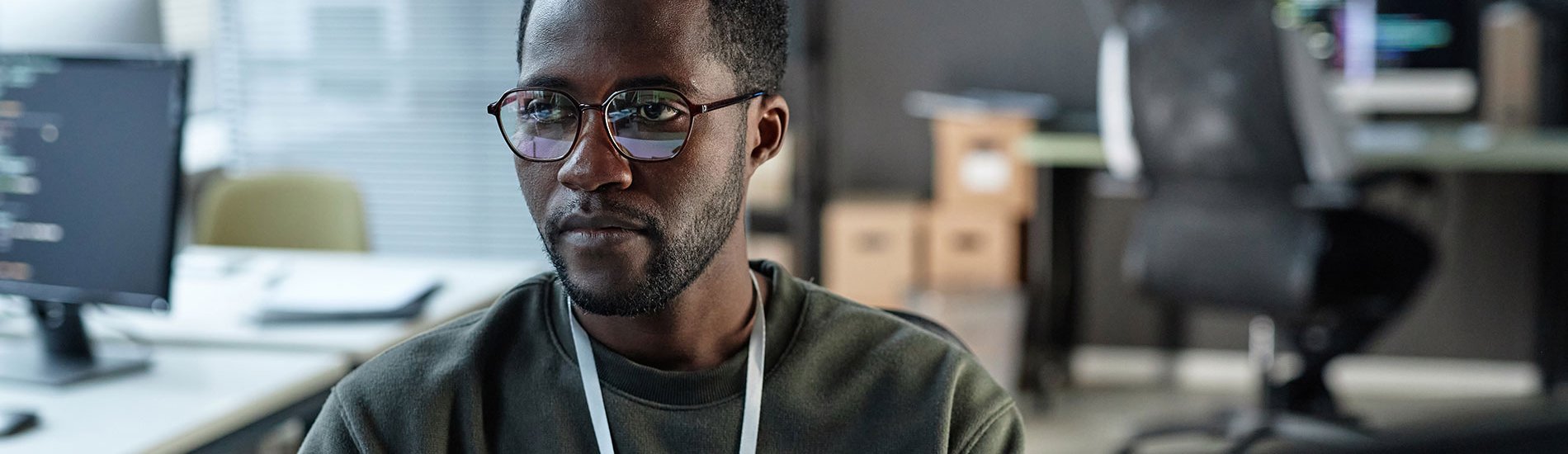
Cybersecurity and software engineering are two of the fastest-growing fields in technology, employing millions of people across the U.S. Professionals in both fields rely on strong problem-solving skills, but the focus of their work differs. Cybersecurity specialists defend systems and data from digital threats, while software engineers design and maintain the applications people use every day.
With $16.6 billion in cybercrime losses reported to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center in 2024, the demand for cybersecurity professionals has been accelerating. Meeting that challenge requires specialized education, which equips individuals with the knowledge and experience they need to protect critical systems.
For anyone weighing cybersecurity versus software engineering for their career, understanding how these two fields and their educational requirements differ is key to choosing the one that best matches the individual’s interests and long-term goals.
What Does a Cybersecurity Program Entail?
A cybersecurity degree program combines technical knowledge with applied learning to prepare students for roles focused on protecting sensitive information and digital infrastructure. Most undergraduate programs are structured as four-year degrees, though the exact time it takes to complete a program can vary depending on a student’s concentration, whether they choose an accelerated program option and whether they attend part time or full time.
Coursework in a cybersecurity program often covers information security, programming, computer networks and database fundamentals. Many programs also emphasize hands-on training through labs, a capstone project and an internship, which provide students with experience that mirrors the real-world challenges they will face as graduates.
With cyberthreats growing in scale and sophistication, cybersecurity graduates are in demand across industries such as government, finance and health care. Common roles for cybersecurity graduates include security analyst, incident responder, penetration tester and consultant. Others advance into policy development or risk management, shaping how organizations approach digital security.
What Does a Software Engineering Program Entail?
A software engineering degree program prepares students to design, build and maintain applications that drive business and daily life. Students gain a strong foundation in computer science and mathematics while learning practical skills related to software design and development. As with a cybersecurity bachelor’s degree program, a software engineering bachelor’s degree program typically requires four years of full-time study to complete, with flexibility for accelerated, part-time or online options.
Typical courses in a software engineering program cover algorithms, data structures, programming languages and software architecture, along with software testing, quality assurance and project management. Electives may explore areas such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing or mobile app design. This mix of theory and applied learning equips students with the skills they’ll need to build and maintain complex software systems.
Team-based projects and capstone experiences provide students with opportunities to apply classroom knowledge in real-world contexts.
Potential roles for software engineering graduates are diverse, ranging from application engineer and systems architect to quality assurance specialist. Their skills are in demand across industries, including technology, finance and health care. Some software engineers pursue opportunities with startups or entrepreneurial ventures, while others join established organizations to build innovative platforms.
Cybersecurity vs. Software Engineering: Program Comparison
Cybersecurity and software engineering programs both provide students with a strong foundation in computer science, but they differ in several areas, including their focus and typical career outcomes.
Meeting Occupational Requirements
Entry-level jobs in both fields typically require a four-year bachelor’s degree. Cybersecurity professionals often also pursue certifications such as the certified information systems security professional (CISSP) or CompTIA’s security plus credential to validate their specialized expertise. Software engineers may continue on to graduate study if they’re interested in advanced research or leadership roles.
Program Curriculum
Cybersecurity programs emphasize system defense, digital forensics, compliance and risk management. Software engineering programs concentrate on software creation through coursework in algorithms, data structures and software architecture. Both involve programming, but with distinct goals: Cybersecurity programs focus on protection, while software engineering programs center on design and innovation.
Skills Developed
Cybersecurity degree programs emphasize skills in risk analysis, cryptography and rapid problem-solving under pressure, preparing students to anticipate and respond to evolving threats. Software engineering degree programs concentrate on skills in coding, system design and collaborative project management, equipping students to create reliable and scalable software.
Both programs help students build problem-solving, analytical thinking and teamwork abilities that apply across the tech industry.
Career Outcomes
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), information security analysts, including cybersecurity analysts, had a median annual salary of $124,910 in 2024. Information security analyst employment is projected to grow 33% between 2023 and 2033.
Software developers had a median annual salary of $131,450 in 2024, per the BLS. Employment growth for that role is projected to be 25% between 2023 and 2033.
Launch a Tech Career in Cybersecurity
Both cybersecurity and software engineering offer rewarding opportunities, but the right choice depends on your career goals. If you’re drawn to defending systems, preventing attacks and managing digital risks, cybersecurity is a growing field with high demand for skilled professionals.
The University at Albany’s Bachelor of Science in Cybersecurity program, which is offered both in person and online, provides students with the knowledge, hands-on training and career preparation needed to step into critical cybersecurity roles. The program emphasizes experiential learning, from internships and independent research to community-based projects, ensuring you graduate with real-world experience.
The program offers four concentrations: cyber defense, cyber risk management and policy, cyber operations and a self-designed track. Students also have the opportunity to pursue an accelerated master’s program, completing graduate-level coursework alongside their bachelor’s studies to advance more quickly into leadership roles.
Learn more about how UAlbany’s program can prepare you for a successful cybersecurity career.

CEHC Launches Revamped Undergraduate Cybersecurity Program

Massry School of Business Lauded as National Center of Academic Excellence in Cyber Defense

Sen. Gillibrand Encourages UAlbany Students to Apply for Federal Cybersecurity Scholarship Program